关于游戏物理实现
基础公式计算
https://blog.51cto.com/u_15273495/5040568
在游戏开发中,有时你可能希望不使用物理引擎来实现一些物理效果。可以通过手动编写代码来模拟这些效果,以下是一些常见方法和示例代码:
1. 运动学公式
使用基本的运动学公式来模拟物体的运动。假设你有一个物体,它的初始位置、速度和加速度是已知的,你可以使用以下公式来计算它的新位置和速度:
- 位置更新公式:
position = position + velocity * deltaTime + 0.5 * acceleration * deltaTime^2 - 速度更新公式:
velocity = velocity + acceleration * deltaTime\
2.手动检测碰撞
https://blog.csdn.net/yhn19951008/article/details/119899092
通过编写代码来检测物体之间的碰撞。以下是一个简单的 AABB (Axis-Aligned Bounding Box) 碰撞检测示例:
1 | bool IsColliding(Rect a, Rect b) |
3. 模拟重力
https://blog.csdn.net/dcs147/article/details/68063421
手动添加重力效果,可以通过每帧更新物体的速度和位置来实现:
1 | Vector3 position; |
4. 阻尼效果
添加阻尼效果来模拟摩擦力或空气阻力:
1 | float damping = 0.98f; // 阻尼系数 |
5. 碰撞响应
手动处理碰撞响应,例如在碰撞时反弹:
1 | void OnCollisionEnter(Collision collision) |
6. 简单力学模拟
手动应用力和转矩:
1 | Vector3 force; |
通过这些方法,你可以在不使用物理引擎的情况下实现一些简单的物理效果。根据实际需求,可以组合使用这些技术来模拟更复杂的物理行为。
圆和矩形碰撞
碰撞检测算法:点和矩形碰撞、点和圆形碰撞、矩形碰撞、圆形碰撞 - zhepama - 博客园
如果要横向判断碰撞的话,判断(x1-x2)的绝对值是否小于或者等于w1/2+w2/2,如果是则横向则有碰撞。纵向判断是一样的,判断(y1-y2)的绝对值是否小于或等于h1/2+h2/2即可。
AABB算法
【Unity】碰撞检测算法及框架实现 - JimmyZou - 博客园
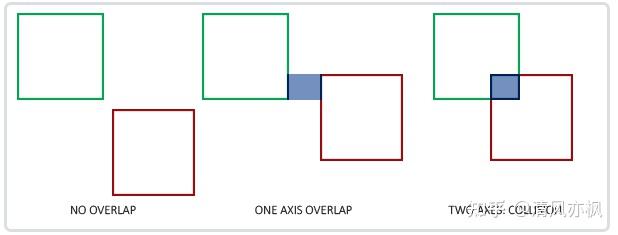
](https://img2024.cnblogs.com/blog/2217860/202407/2217860-20240719213026607-1364733929.png) 当两个碰撞外形进入对方的区域时就会发生碰撞,例如定义了第一个物体的碰撞外形以某种形式进入了第二个物体的碰撞外形。对于AABB来说很容易判断,因为它们是与坐标轴对齐的:对于每个轴我们要检测两个物体的边界在此轴向是否有重叠。因此我们只是简单地检查两个物体的水平边界是否重合以及垂直边界是否重合。如果水平边界和垂直边界都有重叠那么我们就检测到一次碰撞。
当两个碰撞外形进入对方的区域时就会发生碰撞,例如定义了第一个物体的碰撞外形以某种形式进入了第二个物体的碰撞外形。对于AABB来说很容易判断,因为它们是与坐标轴对齐的:对于每个轴我们要检测两个物体的边界在此轴向是否有重叠。因此我们只是简单地检查两个物体的水平边界是否重合以及垂直边界是否重合。如果水平边界和垂直边界都有重叠那么我们就检测到一次碰撞。
1 | GLboolean CheckCollision(GameObject &one, GameObject &two) // AABB - AABB collision |
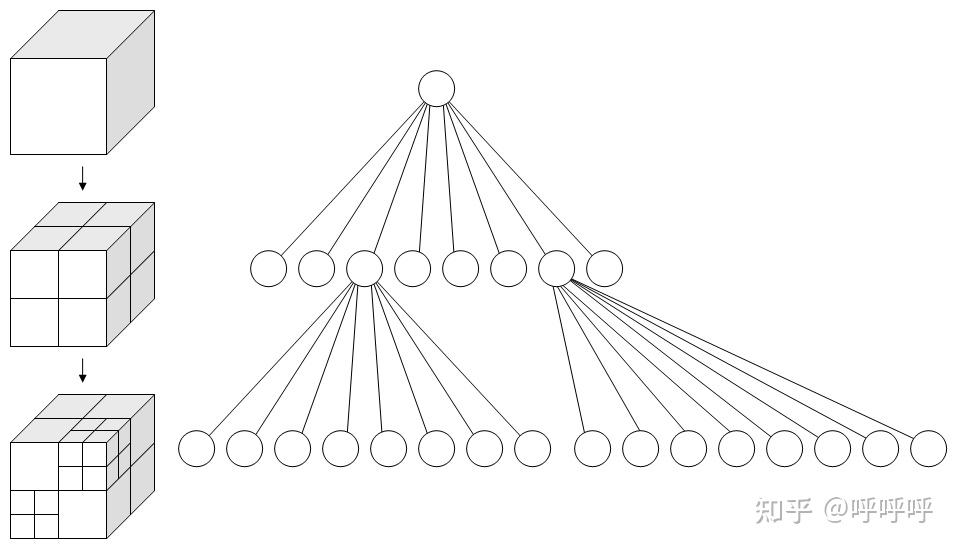
八叉树算法
- 构造八叉树:开始时,将整个三维空间划分为一个大的立方体,作为根节点。然后,递归地将根节点分割成八个子节点,每个子节点代表一个子立方体。这个过程会一直递归下去,直到满足某个终止条件(如达到最大深度或子立方体中的对象数量达到阈值)。
- 插入对象:要将一个对象插入八叉树中,需要找到对象所在的子立方体。从根节点开始,根据对象的位置依次遍历子节点,直到找到合适的子节点。如果子节点不存在,则创建一个新的子节点。将对象插入到该子节点中。如果子节点已经达到终止条件,则根据具体情况进行处理(如将对象存储在该节点中,或进一步细分子节点)。
- 查询对象:要查询八叉树中的对象,可以从根节点开始,根据查询条件判断是否需要遍历子节点。如果查询条件与子节点的范围有重叠,则递归遍历该子节点。如果查询条件与子节点没有重叠,则可以跳过该子节点。